How To Make A Paper Robot That Can Walk
How To Make A Paper Robot That Can Walk. Speaking about its fairly new and unique legs, this robot is equipped with soft C shaped legs. It was tested against a similar robot which was made out of rigid materials.

You can actually build a simple walking robot without no Arduino, Raspberry Pi, or microcontroller involved!
So we now have all the data from the sensor.

Scientists Invent Shapeshifting Origami Robot from ...
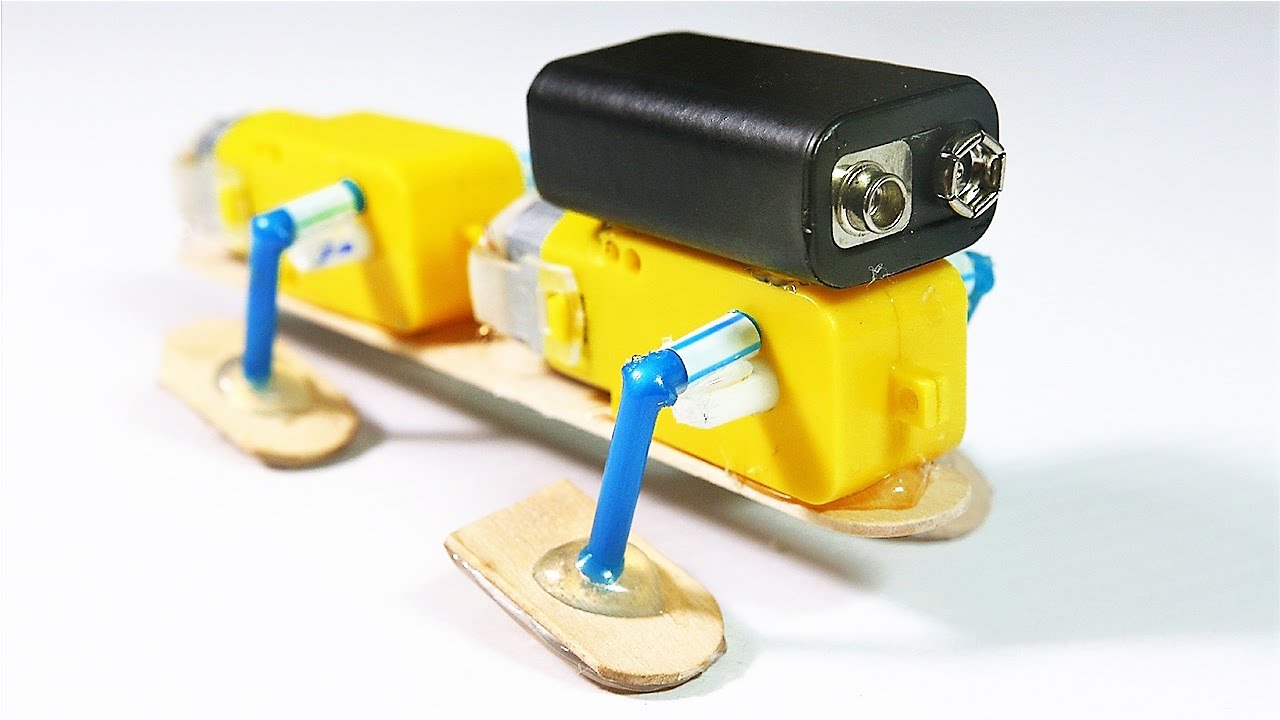
How To Make A Very Simple 4 Legged Walking Robot - YouTube
This DIY Walking Paper Robot Shoots Rubber Bands from Its ...
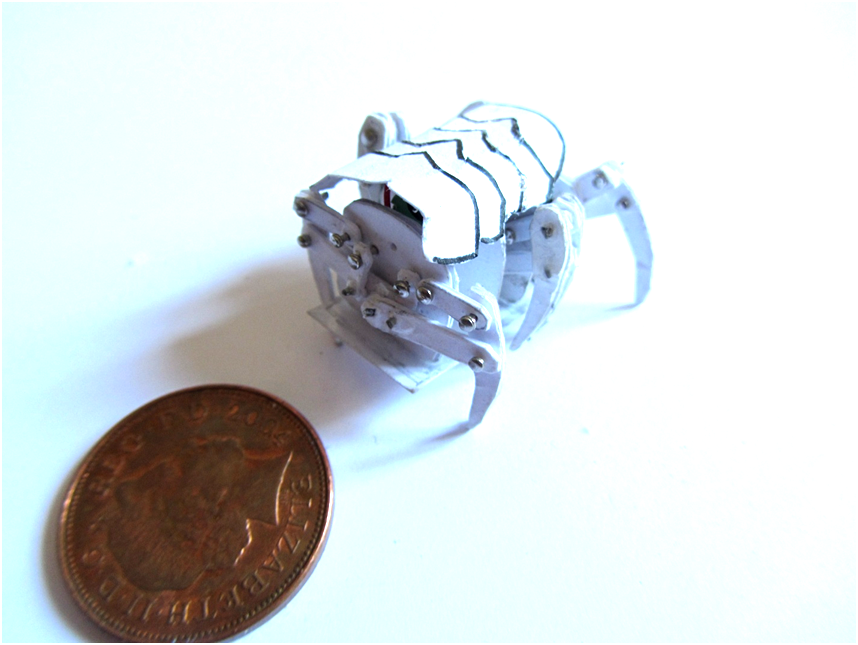
Micro Paper Robots (cyborg Crab) : 8 Steps (with Pictures ...

How to Make A Robot - Robot Beep

Robots Paper Toys - Movable Paper Toys - DIY Paper Craft ...
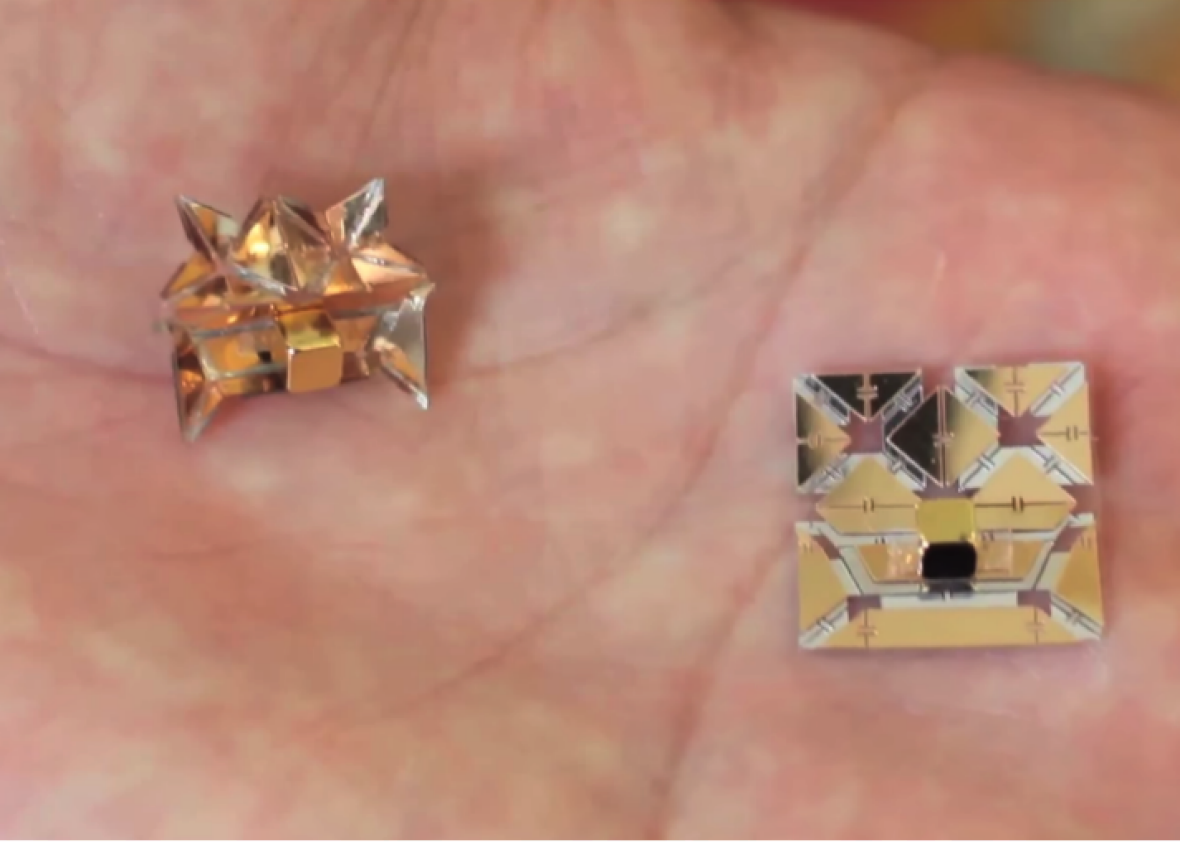
MIT debuts origami robot for future medical and industrial ...
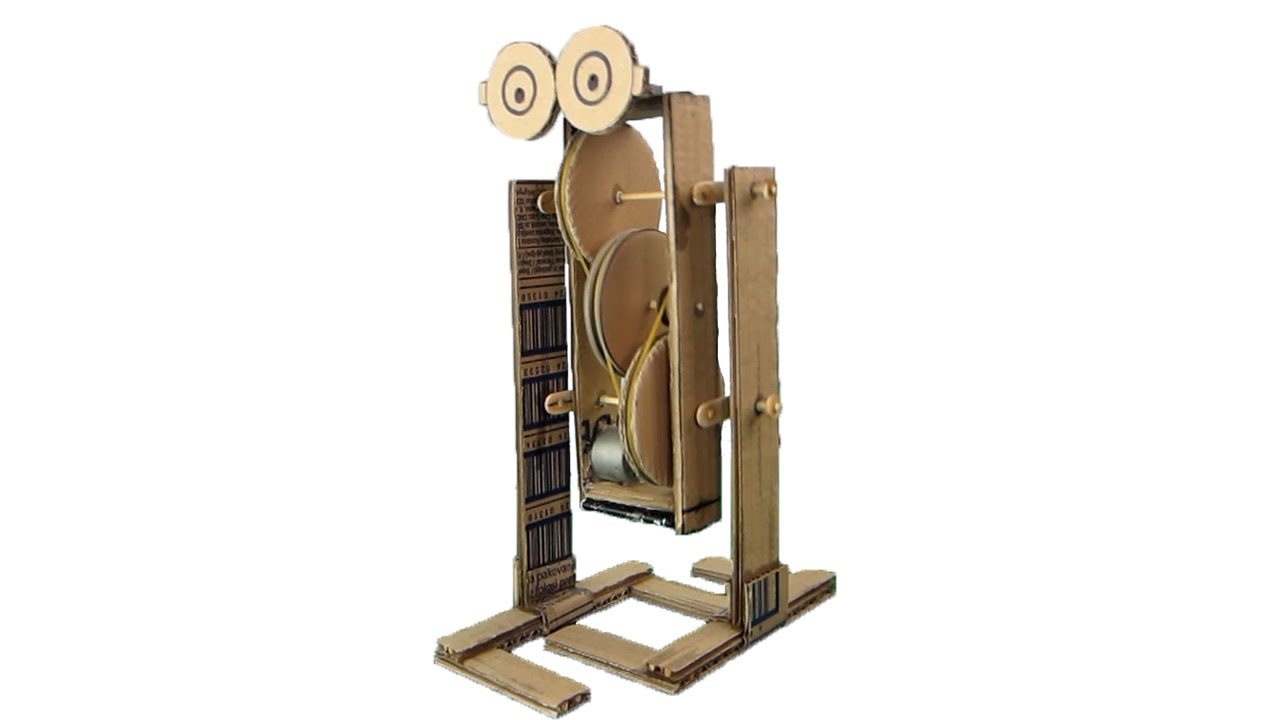

How to Make Walking Robot - YouTube
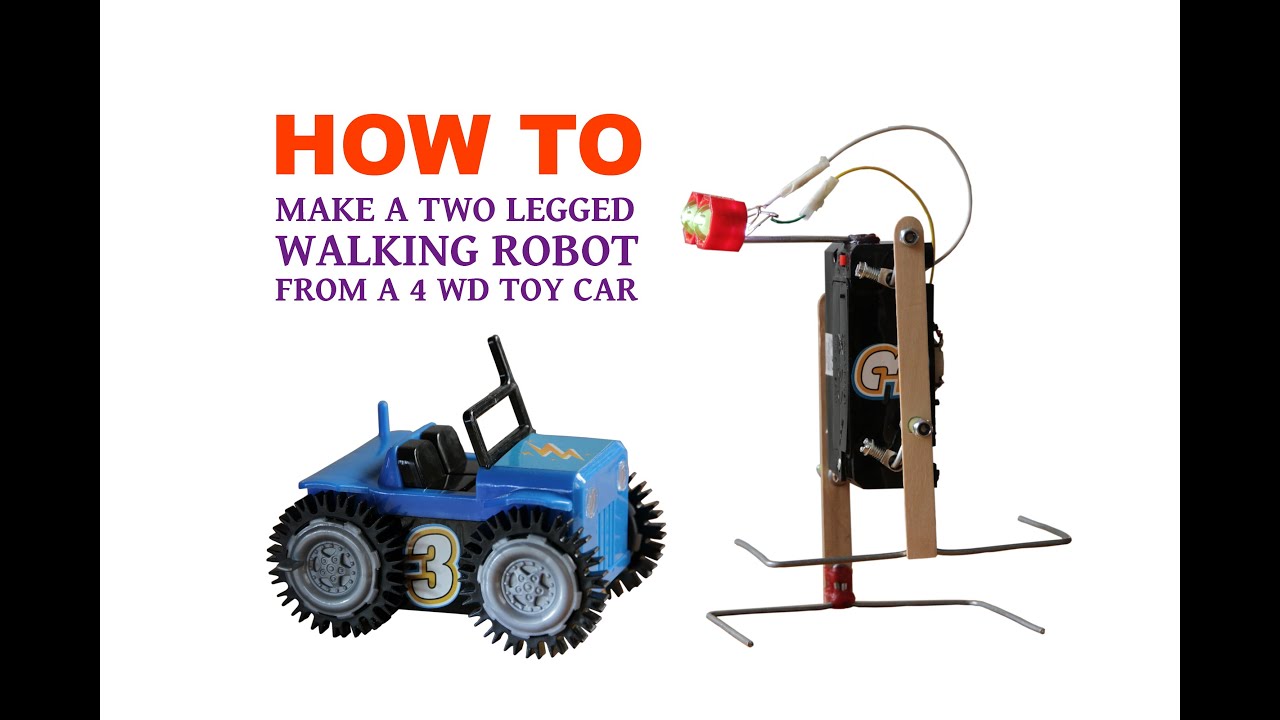
How to Make a Walking Robot From 4 WD Toy Car - YouTube
To make your quadruped walk, you will first need to connect the servomotor controller to the servos. Follow the directions below to make your own water-walking critter using thin wire, and then test its effectiveness by counting how many paper clips it can carry without sinking. Watch the Science Friday video "Stroke of the Water Strider" to learn about a robot that was inspired by insects' ability to travel on the surface of water.
Beautiful How To Make A Paper Robot That Can Walk
Don't let the number of steps fool you into believing otherwise. What to do with this sensor data? If you want to build the paper robot yourself, the plans can be found here. This robot is basically made with a handful of household items and some simple electronics that you can easily pick up at Radioshack.
